The network address can be assigned dynamically (DHCP) or statically (Fixed-IP). It is unique and identifies the device in the network. The correct setting depends on the network in which the device is integrated.
Figure: Network
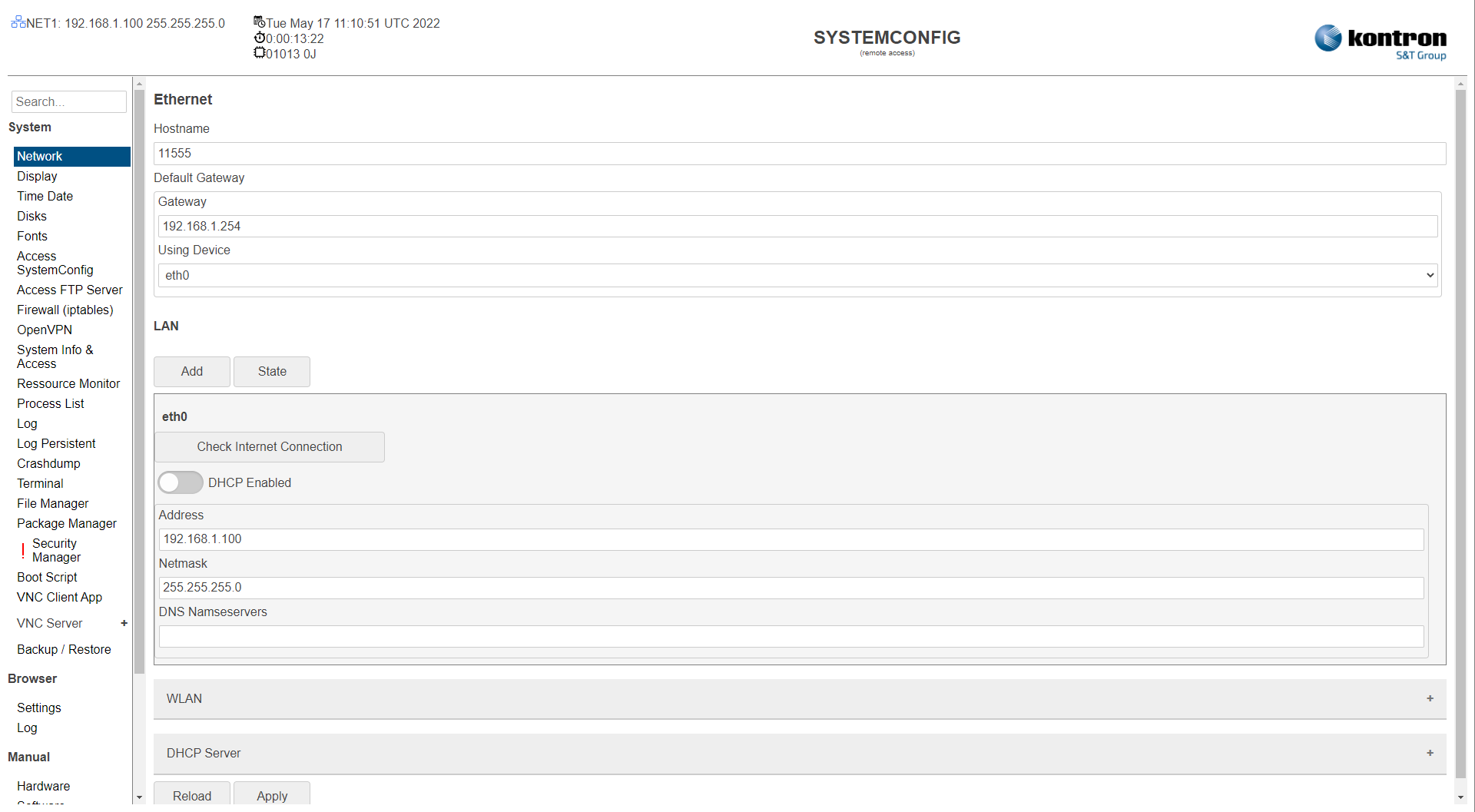
Table: General Network Settings
|
Setting |
Description |
Default |
|---|---|---|
|
Hostname |
Name under which the device is recognized in the network. |
4009986 |
|
DHCP Client Timeout |
Wait time (in secods), on booting device or restarting network, till there is a response from a DHCP server. Only used if a network is configured as dhcp. |
60 |
|
Gateway |
Gateway setting |
192.168.1.254 |
|
Using Device |
Assignment of the gateway setting to an interface. |
Ethernet 1 |
|
Add |
Assignment of additional IP addresses to an Ethernet interface. |
|
|
DHCP Enabled |
Active: Device obtains the IP address from a DHCP server in the network.
|
Inactive |
|
Check Internet Connection |
Checks access to the internet. |
|
|
Address |
Fixed IP address |
Ethernet 1: 192.168.1.100 Ethernet 2: 192.168.2.100 |
|
Netmask |
Network Mask |
255.255.255.0 |
|
DNS Nameserver |
DNS nameserver setting |
|
Table: WLAN Settings
|
Setting |
Description |
Default |
|---|---|---|
|
WLAN Mode |
WLAN Mode for USB WLAN Adapter
|
Off |
|
WLAN AccessPoint Address |
Fixed IP address |
|
|
WLAN AccessPoint Netmask |
Network Mask |
|
|
WLAN Access Point (hostapd.conf) |
Local hostapd configuration file on the system
|
|
|
WLAN Client Address |
Fixed IP address |
|
|
WLAN Client Netmask |
Network Mask |
|
|
WLAN Client DNS nameservers |
DNS nameserver setting |
|
|
WLAN Client SSID |
SSID of the AccessPoint |
|
|
WLAN Client Password |
Password of the AccessPoint |
|
|
Scan |
Search WLAN Network AccessPoint |
|
Table: DHCP Settings
|
Setting |
Description |
Default |
|---|---|---|
|
DHCP Enabled |
On: Devices can obtain the IP address from the Device DHCP server .
|
Off |
|
DHCP server
|
Local dnsmasq configuration file on the system („/etc/dnsmasq.conf“) |
|
|
Verify |
Verify DHCP Server Settings |
|
Table: Bridge Settings
|
Setting |
Description |
Default |
|---|---|---|
|
Switch (Bridge) Enabled |
On: A bridge is a piece of software used to unite two or more network segments. A bridge behaves like a virtual network switch, working transparently (the other machines do not need to know about its existence). Off: Disabled |
Off |
|
|
Active: Device obtains the IP address from a DHCP server in the network.
|
Inactive |
|
|
Fixed IP address |
|
|
Netmask |
Network Mask |
|
|
|
DNS nameserver setting |
|
|
Broadcast |
Broadcast mode enables sending data packets to the broadcast address. |
|
|
|
When you enable STP on a bridge, Linux generates untagged STP packets and drops them on the bridge. When a bridge is attached to a physical interface that also has associated VLAN interfaces, those VLAN interfaces will stop seeing any traffic that is not destined for the MAC address of the physical interface. |
Off |
|
Fd |
Forwarding delay |
0 |
|
Ports |
Included Interfaces in the Switch Config |
|
|
|
View all available ethernet bridges on your server. |
|
|
|
Tracking MAC address of a Bridge |
|
|
|
Display STP Parameter Values of a Bridge. STP stands for Spanning Tree Protocol. |
|
The settings can be saved with the Apply button and directly applied to the system without rebooting or reloaded with the Reload button.
